Big Data
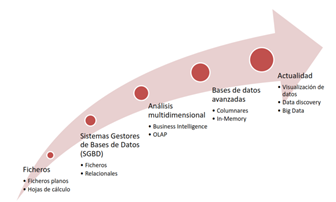
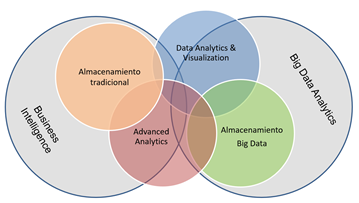
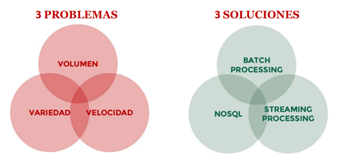
The term “Big Data” was originally associated with three key concepts: large volume of data, variety and complexity of data, and speed of processing.
Over the last decade, the amount of data available has grown exponentially as different types of data sources and origins have been added such as mobile phones and wearables, social networks, RFID tags, cameras, vehicles, TV’s and IoT devices, among others. There is no doubt that there is now a huge volume of data available and therefore the concept of “Big Data” has evolved, becoming more associated with the strategies, methods and tools used for its processing.