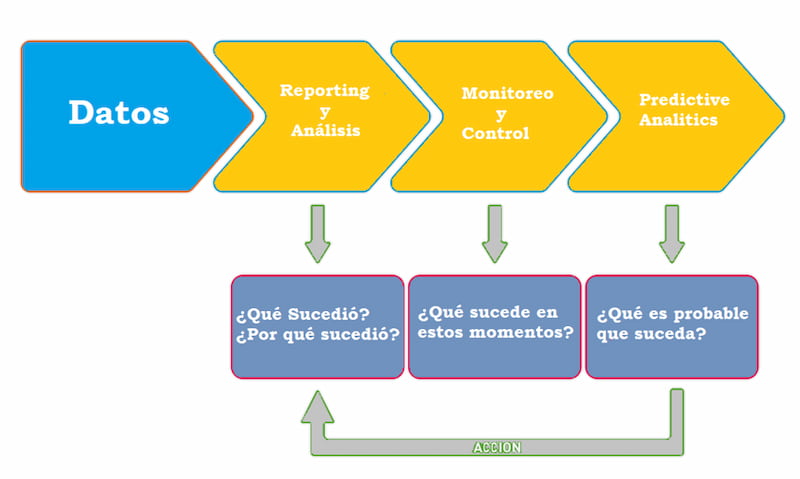
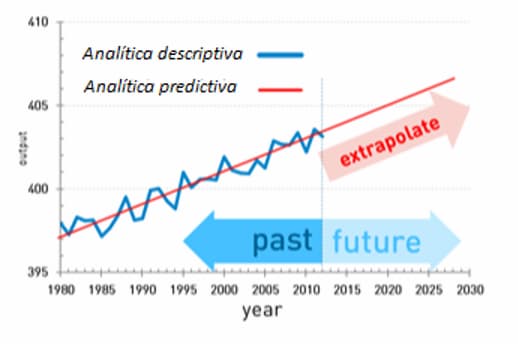
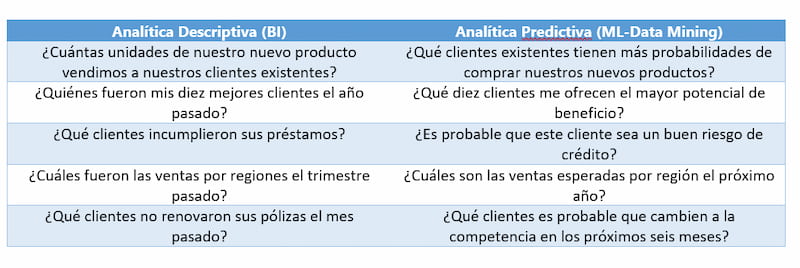
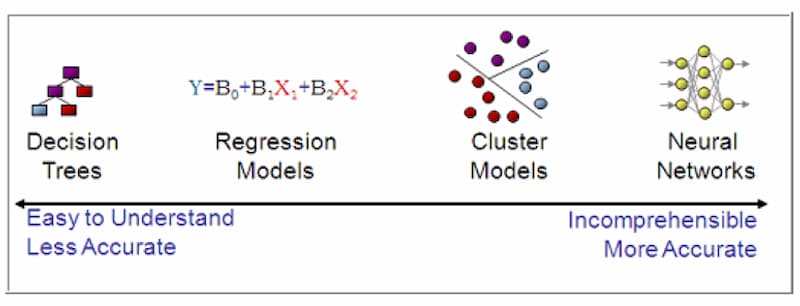
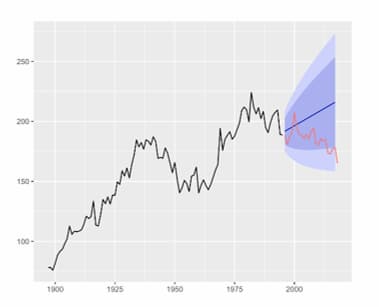
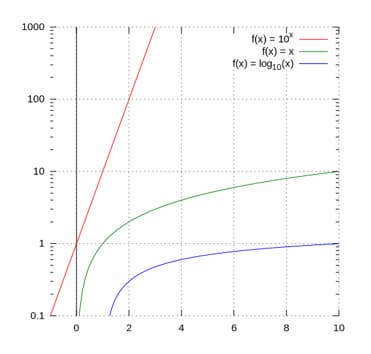
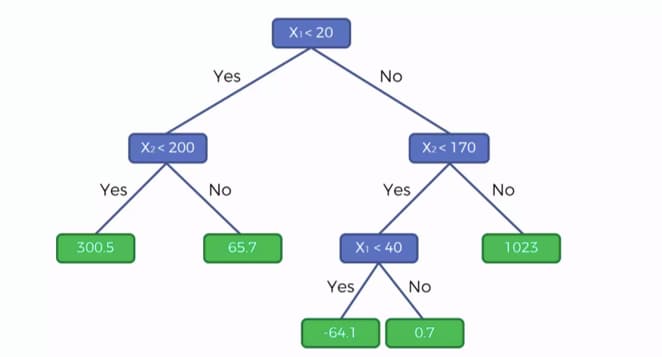
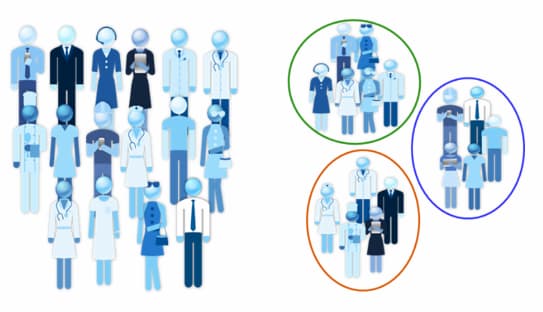
No te pierdas el
WEBINAR
Gratuito
Explicaremos en detalle los contenidos y objetivos del Business Data Master
29/11/2021
18:30 (GTM+1)
Online
BUSINESS DATA MASTER
* Tu información será utilizada exclusivamente para contactarte en relación al Business Data Master. No hacemos spam ni compartimos datos con terceros.